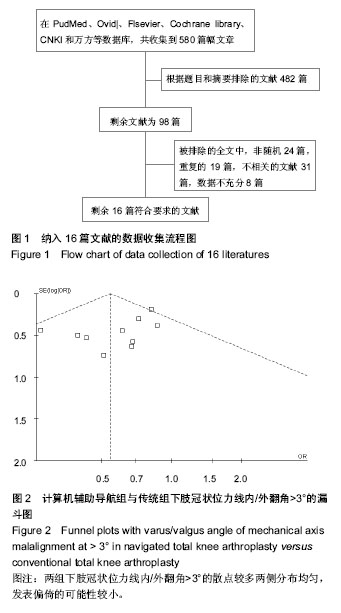
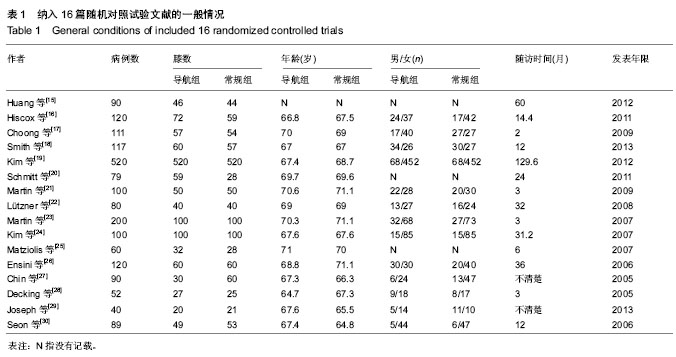
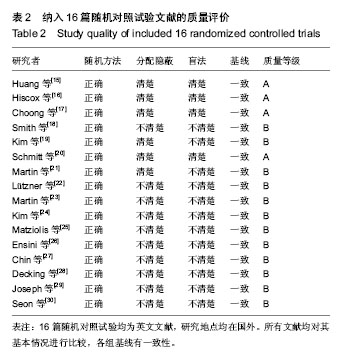
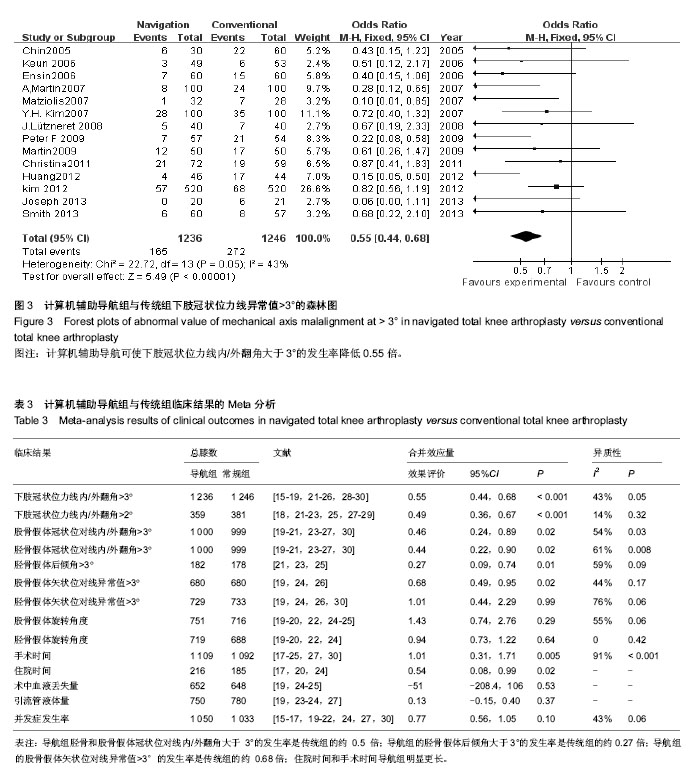
| [1] Ebnezar J, Yogitha Bali M, John R,et al.Role of integrated approach of yoga therapy in a failed post-total knee replacement of bilateral knees.Int J Yoga. 2014;7(2):160- 164.
[2] Fu Y, Wang M, Liu Y, et al. Alignment outcomes in navigated total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2012;20(6):1075-1082.
[3] Hetaimish BM, Khan MM, Simunovic N,et al.Meta-analysis of navigation vs conventional total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1177-1182.
[4] Marques CJ, Daniel S, Sufi-Siavach A,et al.No differences in clinical outcomes between fixed- and mobile-bearing computer-assisted total knee arthroplasties and no correlations between navigation data and clinical scores. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014.
[5] Nakano N, Matsumoto T, Ishida K, et al.Long-term subjective outcomes of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(10):1911-1915.
[6] Keyes BJ, Markel DC, Meneghini RM.Evaluation of limb alignment, component positioning, and function in primary total knee arthroplasty using a pinless navigation technique compared with conventional methods. J Knee Surg. 2013; 26(2):127-132.
[7] Willcox NM, Clarke JV, Smith BR,et al. A comparison of radiological and computer navigation measurements of lower limb coronal alignment before and after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(9):1234-1240.
[8] Cheng T, Zhang G, Zhang X,et al. Imagelessnavigationsystem does not improve component rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Surg Res.2011;171(2):590-600.
[9] Moskal JT, Capps SG, Mann JW,et al.Navigated versus conventional total knee arthroplasty.J Knee Surg.2014; 27(3):235-248.
[10] Molli RG, Anderson KC, Buehler KC, et al.Computer - assisted navi gation software advancements improve the accuracy of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26(3):432-438.
[11] Gøthesen O, Espehaug B, Havelin LI,et al.Functional outcome and alignment in computer-assisted and conventionally operated total knee replacements: a multicentre parallel-group randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(5):609-618.
[12] Kim YH, Kim JS, Choi Y, et al.Computer-assisted surgical navigation does not improve the alignment and orientation of the components in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009,9(1):14-19.
[13] Bauwens K, Matthes G, Wich M, et al.Navigated total knee replacement: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(2):261-269.
[14] Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327(7414): 557-560.
[15] Huang NF, Dowsey MM, Ee E, et al.Coronal Alignment Correlates With Outcome After Total Knee Arthroplasty Five-Year Follow-Up of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2012 ;27(9):1737-1741.
[16] Hiscox CM, Bohm ER, Turgeon TR, et al. Randomized trial of computer-assisted knee arthroplasty: impact on clinicaland radiographic outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1259-1264.
[17] Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD.Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality oflife? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):560-569.
[18] Smith JR, Rowe PJ, Blyth M,et al.The effect of electromagnetic navigation in total knee arthroplasty on knee kinematics during functional activities usingflexible electrogoniometry. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2013;28(1):23-28.
[19] Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS. Computer-navigated versus conventional total knee arthroplasty a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(22):2017-2024.
[20] Schmitt J, Hauk C, Kienapfel H, et al.Navigation of total knee arthroplasty: rotation of components and clinical results in a prospectively randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:16.
[21] Martin A, Sheinkop MB, Langhenry MM, et al.Accuracy of side-cutting implantation instruments for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2009; 17(4):374-381.
[22] Lützner J, Krummenauer F. Computer-assisted and conventional total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br].2008;90(8):1039-1044.
[23] Martin A, Wohlgenannt O, Prenn M, et al. Imageless Navigation for TKA Increases Implantation Accuracy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460:178-184.
[24] Kim YH, Kim JS, Yoon SH.Alignment and orientation of the components in total knee replacement with and without navigation support: a prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(4):471-476.
[25] Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U, et al. A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventionaltotal knee arthroplasty. Three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2): 36-243.
[26] Ensini A, Catani F, Leardini A, et al. Alignments and clinical results in conventional and navigated total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;457:156-162.
[27] Chin PL, Yang KY, Yeo SJ, et al.Randomized control trial comparing radiographic total knee arthroplastyimplant placement using computer navigation versus conventionaltechnique. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(5):618-626.
[28] Decking R, Markmann Y, Fuchs J, et al. Leg axis after computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty: a prospectiverandomized trial comparing computer-navigated and manual implantation. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(3):282-288.
[29] Joseph J, Simpson PM, Whitehouse SL, et al. The use of navigation to achieve soft tissue balance in total kneearthroplasty - a randomised clinical study. Knee. 2013; 20(6):401-406.
[30] Seon JK, Song EK. Navigation-assisted less invasive total knee arthroplasty compared withconventional total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6):777-782.
[31] 张闻,邵俊杰,张先龙.导航辅助全膝关节置换术的精确性及误差分析[J].国际骨科杂志,2007,28(6):359-364.
[32] 董锐,陈述祥,林汉生.计算机导航人工全膝关节置换与传统手术临床效果比较的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(23): 1937-1940.
[33] Matsuda S, Mizu- uchi H, Miura H, et al. Tibial shaft axis do es not always serve as acorrect coronal landmark in total knee ar throplasty for varus knees. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(1) : 56 -62.
[34] Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Jiont Surg Br. 1991;73(5);709-71.
[35] Bathis H, Perlick L, Tingart M, et al. Radiological results of image based and non - image-based computer - assisted total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2004;28(2) : 87-90.
[36] Clayton AW, Cherian JJ, Banerjee S,et al.Does the use of navigation in total knee arthroplasty affect outcomes?J Knee Surg. 2014;27(3):171-175.
[37] Gøthesen Ø, Slover J, Havelin L,et al.An economic model to evaluate cost-effectiveness of computer assisted knee replacement surgery in Norway. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:202.
[38] Kalairajah Y, Simpson D, Cossey AJ, et al .Blood loss after total knee replacement : effects of computer -assisted surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(11):1480-1482. |